We know that arrays are one-dimensional. But there is something more to it that C# has to offer. A powerful feature that allows us to organize data in a grid-like format. If it is more than one-dimensional, it is called multidimensional arrays in C#.
This article explains what multidimensional arrays are, how to use them, followed by some examples for to you understand it in a better way.
Multidimensional Arrays
In C#, a multidimensional array is an array where the data are stored in tabular form or series of 2D grids etc., which is also known as matrix.
We have these types of multidimensional array
Two-Dimensional Array — Data stored as a table/ grid with rows and columns.
Three-Dimensional Array — Data stored as a cube/series of two-dimensional grids.
Higher-Dimensional Array — Rarely used, but C# does allow multiple 3D arrays if needed.
Note: We are not going to focus on this type of array. This is just for information purpose.
Declaring a Multidimensional Array
To create multidimensional array, use comma inside the square brackets.
Declaring A Two-Dimensional Array
int[,] twoDimArray = new int[5,5]Declaring A Three-Dimensional Array
int[,,] threeDimArray = new int[5,5,5];The int[,] here represents a two-dimensional array. Similarly int[,,] represents a three-dimensional array.
Initializing a Multidimensional Array
A multidimensional array can be initialized in two ways:
Default Initialization
In this method, when an array is declared all the elements are initialized to the default value of the data type (e.g. for integers it would 0)
int[,] array = new int[2, 3];Specifying Initial Values
If you don’t want to declare initial values, you can specify them at the time of declaration.
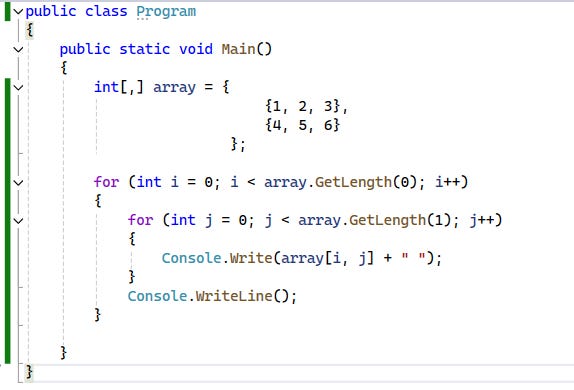
int[,] array = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6}
};Accessing Elements in a Multidimensional Array
Once we declare and initialize values in a multidimensional array, now it’s time to access the elements within.
To access the elements, we are required to specify indices for all dimensions.
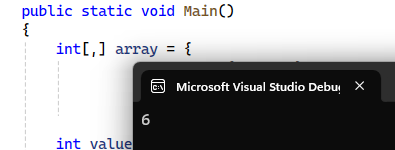
In this example, I have taken a simple 2D array and initialized values in it. Then with the help of array` variable, I am specifying which value I want to access using the index. In this example, I want to access the element at row 1, column 2.
What do you think the answer would be?
If you gave 6 as the answer, then you are absolutely correct my friend!
Iterating Through a Multidimensional Array
Many a times, when you are working on a real project scenario, it is not necessary that you have to pass the index every time to get the data. Many a times, you might need to iterate through an array to traverse all elements to display all the data available.
In this example
I have taken the same array, a 2D array with same elements. Next is something which needs to be understood carefully.
The outer loop where the variable i is declared iterates the rows.
The inner loop with variable j iterates the columns.
The
GetLength()returns the size of a specific dimension.I am printing the value of row and column using their index iterating each time in the array.
Finally, a normal
Console.WriteLine()will add a new line in the console to print the values in the next line.
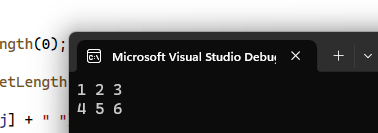
Output
You can try with three dimensional arrays the same way.
Multidimensional Arrays | Real Scenario
Here’s a simple real scenario program for you to understand how it works.
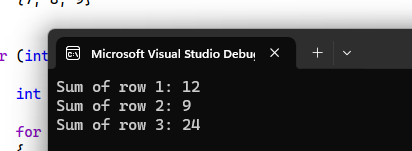
In this example, we are calculating the sum of values of each row in a multidimensional array.
Here, again the same example for you to understand it in a better way.
I’m looping through the rows first.
I have initialized a variable
rowSumwith a default value 0.Then I’m looping through the column.
I am appending the result of
array[i,j]intorowSum.Finally printing the result
rowSumonto a Console.
Output
Jagged Arrays vs. Multidimensional Arrays
C# also supports a special type of array called Jagged Array. These are the array of arrays.
Understand it this way:
Data of Data is called Metadata, similarly in C# array of array is called Jagged Array.
In multidimensional arrays, rows are not allowed to have different lengths. That we can see from each examples above. But guess what, this is not the same case with Jagged Arrays. Here is one example:
int[][] jaggedArray = new int[2][];
jaggedArray[0] = new int[] {1, 2};
jaggedArray[1] = new int[] {3, 4, 5};Jagged arrays are more flexible but may require additional handling for nested arrays of varying lengths.
When to Use Multidimensional Arrays
You can use Multidimensional arrays in the following scenario
When the data is strictly in tabular format like rows and columns.
While storing and processing images — pixels are stored in the form of rows and columns.
Performing mathematical computations with matrices.
Ending Note
Multidimensional arrays provide a handy way to handle complex data. If you understand how to declare, initialize and work with these arrays it would be a piece of cake to handle grid-like data or even complete data.
So, practice, practice, practice!
Like It?
If you enjoy it, feel free to read, clap, and share your thoughts in the comments. Your feedback means a lot!
Buy Me A Coffee ☕
If you’re able, you can buy me a coffee on Buy Me a Coffee. It’s a small gesture that helps us keep the lights on and continue creating content that matters to you. Thank you for considering, and for being part of our community!
Here’s the link 👉 buymeacoffee.com/rohanraobhb